Key Takeaways
- A Cap Table records the equity ownership of founders, investors, employees, and stakeholders, tracking who owns what percentage of the company.
- It monitors ownership distribution, dilution from new investments, and changes in equity over time.
- Key components include shareholder details, share classes (common and preferred stock), stock options, convertible securities, and transaction history (funding rounds, stock grants).
- A well-maintained cap table ensures transparency, helping stakeholders make informed decisions about funding, governance, and growth strategies.
- Regularly updating the cap table is essential for controlling dilution, supporting strategic decisions during investment rounds, and preparing for exit scenarios (acquisitions, IPOs).
How do startups ensure long-term survival in a competitive market? With studies showing only 20% of startups surviving beyond 5 years and just 8% making it past 10, clear financial planning and ownership structures are crucial.
A Cap Table is key to managing equity and ownership dilution, helping founders, investors, and stakeholders track changes as new investments are made.
It provides a transparent view of shareholder interests, enabling informed decisions about funding, governance, and growth strategies.
This blog covers the core elements of a cap table, how to create one, and its strategic importance in startup growth and funding negotiations.
What is a Cap Table?
A Cap Table (Capitalization Table) is a detailed record of a company’s equity ownership, showing the stakes of founders, investors, employees, and other stakeholders.
It tracks who owns what percentage of the company and how ownership is distributed, including stock options, convertible securities, and future equity agreements.
For startups and SMEs, a well-maintained cap table ensures transparency, helping stakeholders understand their stakes during funding rounds, mergers, acquisitions, or exits.
So, how does a cap table work in practice? Let's break down its functions and real-world applications.
How Does a Cap Table Work?
A cap table displays the ownership breakdown of a company, including founders, investors, and other stakeholders who hold equity.
The document typically lists equity holders, the number of shares they own, and the percentage of the company those shares represent.
Example of a Simple Cap Table:
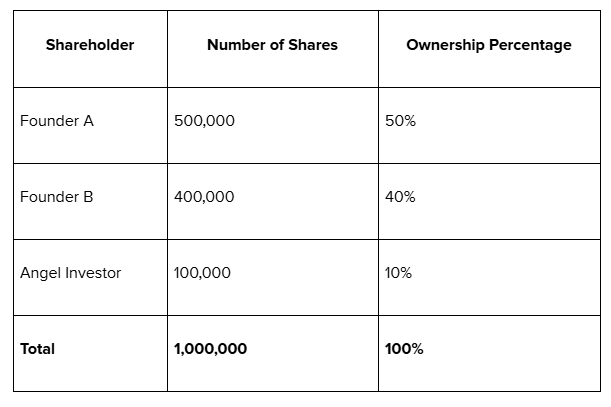
In this example, the company has a total of 1,000,000 shares, and the ownership percentages are directly tied to the number of shares owned by each stakeholder.
As companies look to scale and secure funding, platforms like s45club offer invaluable support by connecting SMEs with investors, ensuring that their cap tables are structured effectively for growth and negotiations.
Now that we understand what a cap table is, let’s break down its structure and key elements for a clearer picture of how it drives effectiveness.
Understanding the Structure and Key Elements of a Cap Table

A cap table provides a detailed overview of a company’s ownership structure, helping founders, investors, and stakeholders track equity distribution and changes over time.
It combines key ownership details, equity types, and transaction history to offer a clear view of how the company’s equity evolves through various stages of funding and growth.
The structure of a cap table typically includes the following core elements:
1. Ownership Details
This outlines the key stakeholders and tracks their respective equity holdings, providing a snapshot of ownership percentages and shares at any given moment.
- Lists equity holders, including founders, investors, employees, and other stakeholders.
- Tracks the number of shares and the corresponding ownership percentage for each party.
- Shows who owns what percentage of the company at any given time.
2. Types of Equity
It outlines the different forms of equity and the specific rights attached to each type, including voting rights and financial preferences.
- Includes different forms of equity such as common stock, preferred stock, and stock options.
- Distinguishes between shareholders' rights, such as voting rights and liquidation preferences.
3. Share Classes
Describes the various classes of shares within the company, each carrying different levels of control and privileges for the shareholders.
- Represents different types of equity, such as Class A or Class B shares.
- Each share class may come with varying levels of voting rights, dividends, and liquidation preferences.
- Preferred stockholders typically receive priority in dividends and during exit events.
4. Equity Event Log
This tracks key equity-related transactions and changes, offering insight into the evolution of ownership and capital flow.
- Records equity-related events such as funding rounds, stock option grants, and convertible note conversions.
- Tracks the changes in ownership stakes over time, providing clarity on the flow of capital and shareholder participation.
5. Valuations
Provides an overview of the company's valuation at various points, assisting in determining future equity pricing and investment decisions.
- Tracks the company’s valuation at each funding round or key milestone.
- Helps assess the price of equity during future rounds and informs exit strategies.
- Provides a benchmark for understanding how the company’s value evolves.
6. Dilution Analysis
Highlights how new equity issuances affect the ownership distribution, helping predict the impact on existing shareholders.
- Shows how new equity issuances impact existing shareholders' ownership percentages.
- Guides decisions on equity allocation and funding strategies for future rounds.
- Helps predict the effect of issuing stock options or raising capital on ownership distribution.
7. Exit Scenarios
This last step shows potential exit scenarios explaining what would happen in the case of a liquidity event.
- Models potential exit scenarios like acquisitions or IPOs.
- Shows how proceeds would be distributed among shareholders in case of a liquidity event.
- Helps stakeholders understand the financial impact and potential returns during an exit.
Creating a cap table might seem complex, but it’s manageable once you understand the process. Here’s how to get started.
How to Create a Cap Table
Creating a cap table involves gathering essential data about shareholders, their equity holdings, and how ownership changes over time.
A well-structured cap table helps ensure clarity and transparency for all stakeholders, particularly during fundraising, negotiations, or when planning for an exit.
Here's a step-by-step guide:
1. List Shareholders
Start by listing all equity holders, founders, employees, investors, and anyone with equity in the company. This list should include full names, equity ownership details, and any relevant notes about the type of equity (e.g., stock options, convertible notes).
2. Determine Total Shares
Knowing the total number of shares issued by the company is critical for calculating the ownership percentages. This total will serve as the denominator for calculating individual ownership percentages.
3. Input Equity Holders' Information
For each shareholder, input the number of shares they own. This step is crucial in maintaining an up-to-date record of ownership.
For example, founders and early investors might own a significant portion of shares, while employees may have stock options or a smaller percentage.
4. Calculate Ownership Percentages
To determine the ownership percentage for each equity holder, divide the number of shares owned by the total number of shares issued by the company. This formula gives each person’s stake in the company.
Formula:
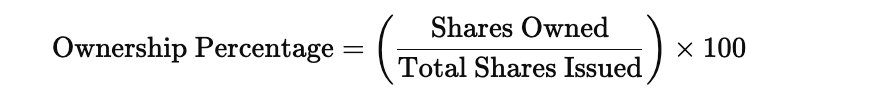
Example: If Founder A owns 500,000 shares out of 1,000,000 total shares, their ownership percentage is:
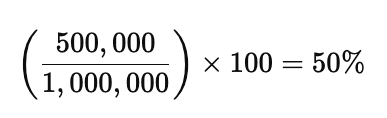
5. Update for Dilution
As a startup grows, its cap table undergoes frequent changes:
- Seed Funding: In early rounds, founders hold most of the equity, and small percentages are allocated to early investors.
- Venture Capital: As the company matures, it may raise multiple funding rounds. With each round, more equity is issued, diluting existing shareholders. For example, after a Series A round, an angel investor’s 10% stake might be diluted to 8%, depending on the new equity issued.
- Employee Stock Options: To incentivize and retain employees, the company might create an option pool, further diluting ownership stakes but motivating team performance.
Cap Tables can be presented in different ways, depending on your needs. Let’s explore the most common formats.
Common Formats of a Cap Table

A cap table can be presented in several formats, depending on the company’s needs and scale. Below are the most common formats:
1. Spreadsheet
Early-stage startups often employ the simplest and most widely used format. It typically includes columns for shareholders' names, the number of shares owned, and the corresponding ownership percentages. This format is flexible and easy to customize.
2. Cap Table Software
Platforms like Carta and EquityEffect automate ownership tracking, dilution calculations, and stock options. These tools are handy for scaling companies with more complex ownership structures.
3. Shareholder Register
A legal document that lists shareholders, their contact information, and the allocation of shares. This format is necessary for regulatory compliance, especially during incorporation or exit planning.
In India, Section 88 of the Companies Act, 2013, mandates companies to maintain a shareholder register for legal and regulatory compliance purposes.
A well-structured Cap Table does more than track ownership. It plays a key role in guiding startup governance and influencing important decisions. Here’s why it matters.
Strategic Importance of Cap Tables in Startup Governance
A cap table is not only a financial tool but also a governance document. It provides transparency regarding who controls the company, which is crucial for decision-making processes.
It is also used to assess the company’s ownership structure and ensure that power is distributed appropriately between founders, investors, and key employees.
- Power Dynamics: If one investor or founder holds a disproportionate amount of equity, they may exert more control over the company’s direction. This is important for avoiding conflicts and ensuring that decisions align with the startup's goals.
- Employee Retention: A clear stock option plan within the cap table helps ensure that employees are motivated and feel invested in the company’s future success.
- Investor Confidence: Investors are more likely to engage with a startup that has a well-structured cap table, as it indicates professionalism and good governance practices.
For businesses scaling up, platforms like S45 can support governance by connecting SMEs with mentors and experienced investors who guide effective management of their cap tables.
How S45 Supports Startup Funding and Growth
At S45, we empower founders to accelerate growth while preserving control and their hard-earned legacy. Focused on high-growth sectors, we help founders achieve their vision and build lasting success. Here's how we support them:
- Smart Capital Timing: S45 Club helps assess when to bring in external capital, whether for structured funding, secondary exits, or pre-IPO rounds, aligning with your company’s growth cycle.
- In-Depth Due Diligence: Get an investor’s perspective on your company's fundamentals, valuation drivers, and cap table hygiene, ensuring you're always pitch-ready.
- Access to High-Quality Deal Flow: Connect with exclusive pre-IPO and late-stage opportunities that are typically reserved for insider networks.
- Risk Clarity: Evaluate trade-offs like dilution, liquidity, and exit complexity before committing to any funding path.
- Long-Term Equity Advisory: S45 Club provides strategic guidance on ESOP liquidity, partial exits, and institutional capital, helping you build for the future, not just the next round.
Want to build for the long term? Partner with S45 and discover how strategic funding can propel your startup toward sustained growth and success.
Conclusion
A well-structured cap table is crucial for startups, offering a clear view of equity ownership and ensuring transparency for founders, investors, and employees. It helps manage ownership, track dilution, and make informed decisions during funding rounds.
Keeping your cap table accurate enables strategic planning, optimizes capital allocation, and supports sustainable growth, whether you're in the early stages or preparing for a major funding round.
Ready to learn from founders who've been there? Join the S45 community to exchange strategies, share insights, and grow together.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: How does a cap table help during a funding round?
A: A cap table provides a clear view of ownership before and after a funding round, helping investors assess the impact of new capital on existing shareholders. It ensures transparency in how much equity is being offered and at what valuation.
Q: What is the role of a convertible note in a cap table?
A: A convertible note is a type of short-term debt that can convert into equity, usually during a future funding round. The cap table tracks this conversion, showing how the debt will be converted into shares and its impact on ownership percentages.
Q: How does dilution affect decision-making in a startup?
A: Dilution reduces a shareholder's ownership percentage when new equity is issued, which can impact control over decision-making. Founders must manage dilution carefully to avoid losing decision-making power or alienating key stakeholders.
Q: What happens if a shareholder wants to sell their shares?
A: If a shareholder wants to sell their shares, the cap table helps identify how much equity they own and whether there are any restrictions (e.g., right of first refusal or lock-up periods). It’s crucial for understanding the potential impact on ownership distribution.
Q: How does a cap table assist in employee retention?
A: A cap table tracks employee stock options, showing how employees' potential equity stakes evolve over time. This transparency helps retain talent by demonstrating the long-term value of their stock options and aligning their interests with the company’s success.